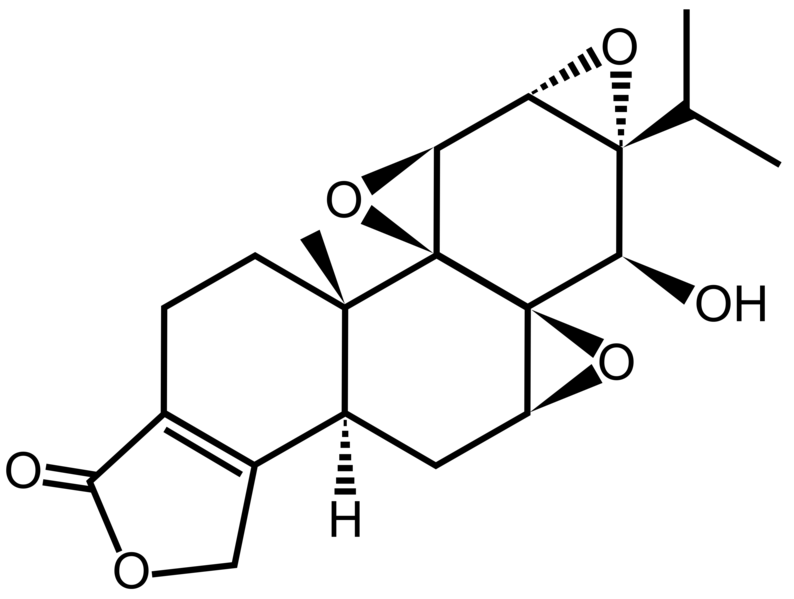
Triptolide is a diterpenoid epoxide found in the Thunder God Vine, Tripterygium wilfordii. It has in vitro and in vivo activities againstmouse models of polycystic kidney disease[1] and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pancreatic_cancer” rel=”nofollow”>pancreatic cancer, but its physical properties limit its therapeutic potential.[2] Consequently, a synthetic prodrug, minnelide, is being studiedclinically instead.[2]
A little-known plant with a truly bizarre name is now making headlines as a cancer killer, with the compound of the plant vanishing tumors in mice with pancreatic cancer. Known as the ‘thunder god vine’ or lei gong teng, the Chinese plant is actually integrated into Chinese medicine and has been used for ages in remedying a number of conditions including rheumatoid arthritis.
According to the new research out of the University of Minnesota’s Masonic Cancer Center, the thunder god plant compound led to no signs of tumors after a 40 day period — even after discontinuing the treatment. Published in the journal Science Translational Medicine
http://stm.sciencemag.org/content/4/156/156ps21.full?sid=5203733d-ae1d-438e-9d36-b8bd9f16cd8d
Pancreas Cancer Meets the Thunder God
- Sunil R. Hingorani and
- John D. Potter
Sci Transl Med 17 October 2012 4:156ps21. DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004956
- Rohit Chugh,et al
Sci Transl Med 17 October 2012 4:156ra139. DOI:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004334
and funded by the National Institutes of Health, even the scientists working on the project were stunned by the anti-cancer properties of the compound. Known to contain something known as triptolide, which has been identified as a cancer fighter in previous research, it is thought to be the key component that may be responsible for the anti-tumor capabilities.
http://thearrowsoftruth.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/thunder-god-vine-stalk_medium-300×199.jpg” width=”300″ height=”199″ />
And just like with numerous other powerful substances like turmeric and ginger, mainstream science is still slowly confirming what many traditional practitioners have known for their entire lives. This is, of course, due to the fact that there is simply no moneyfor major corporations in researching the healing powers of natural herbs and compounds such as the compound found in the thunder god vine. Turmeric and ginger, for example, have been found to be amazing anti-cancer substances that are virtually free compared to expensive and dangerous cancer drugs.
References
- Leuenroth, Stephanie (2007). “Triptolide is a traditional Chinese medicine-derived inhibitor of polycystic kidney disease”.PNAS104 (11): 4389-4394. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700499104. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
- Chugh, Rohit (2012). “A Preclinical Evaluation of Minnelide as a Therapeutic Agent Against Pancreatic Cancer”. Science Translational Medicine4 (156): 156ra139. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004334. Retrieved 18 October 2012.
The article is 2012-2013 based and reader discretion is sought to ascertian the stage of approval
Breast Cancer Drugs in Late-Stage Development/Recently Approved

Afinitor® (everolimus)
http://newdrugapprovals.wordpress.com/2013/04/27/drug-spotlight-afinitor-everolimus-novartis/
Sponsor: Novartis
Method of Action: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor
Indications/Phase of Trial: Hepatocellular carcinoma; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer first-line and second-line; lymphoma; nonfunctional carcinoid tumor (Phase III; all new indications)
Approved in July in U.S., EU for advanced hormone-receptor-positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor Receptor 2-negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer with exemestane in postmenopausal women who have already received certain other medicines for their cancer
Approved earlier for adults with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET) that cannot be treated with surgery; adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) when certain other medicines have not worked; adults with angiomyolipoma, seen with tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), when surgery is not required immediately; and adults and children with TSC who have a brain tumor called subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) that cannot be removed completely by surgery
Avastin (Bevacizumab; RG435)
Sponsor: Roche/Genentech
Method of Action: Monoclonal antibody; Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor
Indications/Phase of Trial: U.S.: Relapsed ovarian cancer, platinum-sensitive (Registration); first-line metastatic breast cancer and first-line metastatic ovarian cancer (both Phase III).
EU: Relapsed platinum-resistance ovarian cancer (Phase III)
Metastatic colorectal cancer, treatment beyond progression (Registration); adjuvant breast cancer, HER2- and HER2+; adjuvant NSCLC; first-line glioblastoma (GBM) multiforme; high-risk carcinoid (all Phase III)
Approved for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) when started with the first or second intravenous 5-FU–based chemotherapy for metastatic cancer; advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with carboplatin and paclitaxel in people who have not received chemotherapy for their advanced disease; metastatic RCC (mRCC) with interferon alfa; and GBM in adult patients whose cancer has progressed after prior treatment. Effectiveness based on tumor response, as no data have shown whether Avastin improves disease-related symptoms or survival in people previously treated for GBM
Approval conditionally granted in 2008 and withdrawn November 2011 for HER2- metastatic breast cancer (mBC) with Paclitaxel
Buparlisib (BKM120)
Sponsor: Novartis
Method of Action: Pan-PI3K inhibitor
Indications/Phase of Trial: mBC (Phase III and confirmatory Phase I/II); with Fulvestrant, in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive HER2- locally advanced or mBC which progressed on or after aromatase inhibitor (AI) treatment (Phase III; BELLE-2 study recruiting as of November 2012); with Fulvestrant, in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive HER2- AI-treated, locally-advanced or mBC who progressed on or after mTOR inhibitor-based treatment (Phase III; BELLE-3 study, recruiting as of October 2012); with Paclitaxel in patients with HER2- inoperable locally advanced or mBC, with or without PI3K pathway activation (Phase III; BELLE-4 study, recruiting as of November); metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC; Phase II; recruiting as of October); recurrent glioblastoma (Phase II; recruiting as of November); recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (Phase II; recruiting as of October); endometrial cancer (Phase I/II); NSCLC (Phase I/II); prostate cancer (Phase I/II); GBM multiforme (Phase I/II); with Fulvestrant in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer (Phase I); previously treated advanced colorectal cancer (Phase I)
Faslodex (Fulvestrant Injection)
Sponsor: AstraZeneca
Method of Action: Estrogen receptor antagonist
Indications/Phase of Trial: First line HR+ mBC (Phase III; FALCON study commenced Oct. 29)
Approved for HR+ mBC in women who have experienced menopause and whose breast cancer has worsened after they were treated with antiestrogen medications
Herceptin (Trastuzumab; RG597)
Sponsor: Roche, in partnership with Halozyme
Method of Action: Humanized monoclonal antibody designed to target and block the function of HER2+
Indications/Phase of Trial: EU: Early HER2+ breast cancer, subcutaneous formulation (Registration)
Approved for early-stage HER2+ breast cancer that has spread into the lymph nodes, and HER2+ breast cancer that has not spread into the lymph nodes and is estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor-negative (ER-/PR-) or have one high-risk feature. High-risk is defined as estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor-positive (ER+/PR+) with one of the following features: tumor size >2 cm, age <35 years, or tumor grade 2 or 3. Can be used with Adriamycin® (doxorubicin), Cytoxan® (cyclophosphamide), and either Taxol® (paclitaxel) or Taxotere® (docetaxel); or with Taxotere and Paraplatin® (carboplatin); or alone after treatment with multiple other therapies, including an anthracycline (Adriamycin)-based chemotherapy
Also approved alone for the treatment of HER2+ breast cancer in patients who have received one or more chemotherapy courses for metastatic disease; and with paclitaxel for first-line treatment of HER2+ mBC
Iniparib (Tivolza; BSI-201; SAR240550)
Sponsor: Sanofi, through acquisition of original developer BiPar Sciences
Method of Action: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitor
Indications/Phase of Trial: Stage IV squamous NSCLC (Phase III; NME); solid tumors such as sarcoma and breast, uterine, lung, and ovarian cancers (Phase I/II)
Phase III trial in breast cancer failed January 2011 by failing to improve survival and progression-free survival (PFS) in breast cancer patients
Nexavar® (Sorafenib)
http://newdrugapprovals.wordpress.com/2013/07/16/nexavar-sorafenib/
Sponsor: Onyx Pharmaceuticals
Method of Action: Dual-action inhibitor that targets RAF/MEK/ERK pathway in tumor cells and tyrosine kinases
Indications/Phase of Trial: Liver cancer adjuvant (Phase III; STORM study); kidney cancer adjuvant (Phase III; SORCE/ASSURE study); thyroid cancer monotherapy (Phase III; DECISION study); breast cancer with capecitabine (Phase III; RESILIENCE study)
Approved for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and RCC
Perjeta (Pertuzumab; RG1273)
Sponsor: Roche/Genentech
Method of Action: HER2/neu receptor antagonist
Indications/Phase of Trial: EU: With Herceptin and docetaxel chemotherapy for previously-untreated HER2+ mBC or locally recurrent, inoperable breast cancer in patients who have not received previous treatment or whose disease has returned after treatment in the early-stage setting (Registration)
U.S.: Approved June 2012 for HER2+ mBC with Herceptin (trastuzumab) and docetaxel, in patients who have not received prior anti-HER2 therapy or chemotherapy for metastatic disease
Switzerland: Approved August 2012 for HER2+ breast cancer with Herceptin (trastuzumab) and docetaxel in patients with advanced or locally recurring breast cancer that has not previously been treated with chemotherapy
Ridaforolimus (MK-8669; AP23573; formerly Deforolimus)
Sponsor: Merck, under exclusive worldwide license agreement with Ariad Pharmaceuticals
Method of Action: Oral inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor (mTOR)
Indications/Phase of Trial: Maintenance therapy for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcomas after at least four chemotherapy cycles (under review after receiving Complete Response letter from FDA in June; NME); breast cancer with exemestane, compared to breast cancer with dalotuzumab and exemestane (Phase II; recruiting as of November); advanced head and neck cancer, NSCLC and colon cancer, with cetuximab (Phase II); pediatric patients with advanced solid tumors (Phase I; recruiting as of September); with dalotuzumab in pediatric patients with advanced solid tumors (Phase I; recruiting as of August); advanced RCC, with vorinostat (Phase I; recruiting as of October 2012); breast cancer, with dalotuzumab (Phase I: recruiting as of September); endometrial and ovarian cancers, with paclitaxel and carboplatin (Phase I; recruiting as of September 2012); advanced cancer, with MK-2206 and MK-0752 (Phase I: recruiting as of September 2012); advanced cancer, with dalotuzumab, MK-2206 and MK-0752 (Phase I: recruiting as of August 2012)
Tivozanib (ASP4130; AV-951)
Sponsor: Aveo Oncology and Astellas
Method of Action: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; inhibits VEGF receptor 1, 2, and 3
Indications/Phase of Trial: U.S.: Advanced RCC (Registration; NDA filed September 2012); tivozanib biomarkers in solid tumors (Phase II; BATON study); stage IV metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), with mFOLFOX6, and compared with bevacizumab and mFOLFOX6 (Phase II; recruiting as of November); additional data as first-line therapy for advanced RCC, followed by sunitinib (Phase II; TAURUS study, enrollment initiated in October 2012); advanced solid tumors, with capecitabine (Xeloda®; Phase I; recruiting as of October)
EU: Advanced RCC (Phase III)
Trastuzumab-DM1 (T-DM1; Trastuzumab emtansine; RG3502)
Sponsor: Roche, with linker technology developed by ImmunoGen
Method of Action: Antibody-drug conjugate, consisting of the antibody trastuzumab and the chemotherapy DM1 attached via a stable linker
Indications/Phase of Trial: U.S.: HER2+, unresectable locally-advanced or mBC who have received prior treatment with Herceptin (trastuzumab) and a taxane chemotherapy (Registration; Priority review approved Nov. 7; action date Feb. 26, 2013)
EU: Marketing Authorization Application for HER2+ mBC accepted for review by European Medicines Agency
Tyverb/Tykerb (lapatinib)
Sponsor: GlaxoSmithKline
Method of Action: Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (Her2) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) dual kinase inhibitor
Indications/Phase of Trial: mBC with trastuzumab (Registration); breast cancer, adjuvant therapy (Phase III); Gastric cancer (Phase III); head & neck squamous cell carcinoma, resectable disease (Phase III)
Xgeva (denosumab)
Sponsor: Amgen, with commercialization by GlaxoSmithKline in countries where Amgen has no presence
Method of Action: Fully human monoclonal antibody that specifically targets a ligand known as RANKL that binds to a receptor known as RANK
Indications/Phase of Trial: Delay or prevention of bone metastases in breast cancer (Phase III); delay or prevention of bone metastases in prostate cancer (Phase III)
Approved for prevention of fractures in men with advanced prostate cancer
Rejected in April for supplemental Biologics License Application to treat men with CRPC at high risk of developing bone metastases
Yondelis® (trabectedin)
Sponsor: Johnson & Johnson; developed in collaboration with PharmaMar
Method of Action: Binds to minor groove of DNA, interfering with the cell division and gene transcription processes, as well as DNA’s repair machinery
Indications/Phase of Trial: U.S.: Locally advanced or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma excluding leiomyosarcoma and liposarcoma who have relapsed or are refractory to standard-of-care treatment (Phase III; recruiting as of November); soft tissue sarcoma, excluding liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma (L-type sarcoma), in previously-treated patients who cannot be expected to benefit from currently available therapeutic options (Phase III; recruiting as of November); locally advanced or metastatic L-sarcoma (liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma) who were previously treated with at least an anthracycline and ifosfamide-containing regimen, or an anthracycline-containing regimen and one additional cytotoxic chemotherapy regimen, compared with dacarbazine group (Phase III; recruiting as of November); breast cancer and pediatric tumors (Phase II); Advanced malignancies and liver dysfunction (Phase I; recruiting as of November)
EU: Approved for advanced or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma, and for relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer, with DOXIL®/Caelyx®
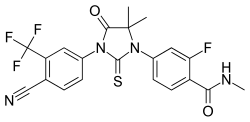
Xtandi® Capsules (Enzalutamide; formerly MDV3100)
Sponsor: Medivation in collaboration with Astellas
Method of Action: Androgen receptor inhibitor
Indications/Phase of Trial: Prechemotherapy CRPC in patients who have failed luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analog treatment only, as well as patients who have failed both LHRH analog and anti-androgen treatment. (Phase III; PREVAIL study); prostate cancer neoadjuvant therapy (Phase II); prechemo metastatic prostate cancer in Europe (Phase II; TERRAIN); prechemo metastatic and nonmetastatic prostate cancer patients in U.S. (Phase II; STRIVE); prostate cancer Hormone-naïve (Phase II; ASPIRE); prostate cancer with docetaxel (Phase I); breast cancer (Phase I)
EU: Marketing Authorization Application submitted June 2012 to European Medicines Agency, for patients with metastatic CRPC who have received docetaxel-based chemotherapy
Japan: Metastatic CRPC who have received docetaxel-based chemotherapy (Phase II)
Approved Aug. 31 for patients with metastatic CRPC who have previously received docetaxel. As a post-marketing requirement, Medivation and Astellas agreed to conduct an open-label safety study of Xtandi (160 mg/day) in patients at high risk for seizure, with data to be submitted to FDA in 2019


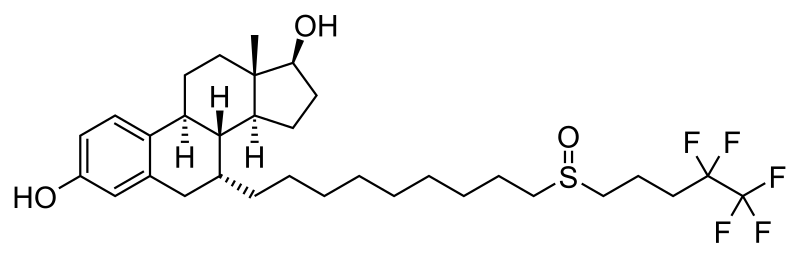
 The conversion of cholesterol into 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes the growth of hormone-dependent breast cancer
The conversion of cholesterol into 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes the growth of hormone-dependent breast cancer
From Cholesterol to Breast Cancer
]]>
capecitabine
154361-50-9
- R-340, Ro-09-1978, Xeloda
pentyl [1-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-5-fluoro-2-oxo-1H-pyrimidin-4-yl]carbamate

MONDAY Sept. 16, 2013 — The first generic version of the oral chemotherapy drug Xeloda (capecitabine) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat cancers of the colon/rectum or breast, the agency said Monday in a news release.
This year, an estimated 142,820 people will be diagnosed with cancer of the colon/rectum, and 50,830 are predicted to die from the disease, the FDA said, citing the U.S. National Cancer Institute. An estimated 232,340 women will be diagnosed with cancer of the breast this year, and some 39,620 will die from it.
The most common side effects of the drug are diarrhea, vomiting; pain, redness, swelling or sores in the mouth; fever and infection, the FDA said.
The agency stressed that approved generics have the same high quality and strength as their brand-name counterparts.
License to produce the generic drug was given to Israel-based Teva Pharmaceuticals. The brand name drug is produced by the Swiss pharma firm Roche.
Capecitabine (INN) /keɪpˈsaɪtəbiːn/ (Xeloda, Roche) is an orally-administeredchemotherapeutic agent used in the treatment of metastatic breast andcolorectal cancers. Capecitabine is a prodrug, that is enzymatically converted to 5-fluorouracil in the tumor, where it inhibits DNA synthesis and slows growth of tumor tissue. The activation of capecitabine follows a pathway with three enzymatic steps and two intermediary metabolites, 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine (5′-DFCR) and 5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine (5′-DFUR), to form 5-fluorouracil

Indications
Capecitabine is FDA-approved for:
- Adjuvant in colorectal cancer Stage III Dukes’ C – used as first-line monotherapy.
- Metastatic colorectal cancer – used as first-line monotherapy, if appropriate.
- Metastatic breast cancer – used in combination with docetaxel, after failure of anthracycline-based treatment. Also as monotherapy, if the patient has failed paclitaxel-based treatment, and if anthracycline-based treatment has either failed or cannot be continued for other reasons (i.e., the patient has already received the maximum lifetime dose of an anthracycline).
In the UK, capecitabine is approved by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) for colon and colorectal cancer, and locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer.[1] On March 29, 2007, the European Commission approved Capecitabine, in combination with platinum-based therapy (with or without epirubicin), for the first-line treatment of advanced stomach cancer.
Capecitabine is a cancer chemotherapeutic agent that interferes with the growth of cancer cells and slows their distribution in the body. Capecitabine is used to treat breast cancer and colon or rectum cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Formulation
Capecitabine (as brand-name Xeloda) is available in light peach 150 mg tablets and peach 500 mg tablets.
- Lacy, Charles F; Armstrong, Lora L; Goldman, Morton P; Lance, Leonard L (2004). Lexi-Comp’s Drug Information Handbook (12th Edition). Lexi-Comp Inc. ISBN 1-59195-083-X
- Fischer, David S; Knobf, M Tish; Durivage, Henry J; Beaulieu, Nancy J (2003). The Cancer Chemotherapy Handbook (6th Edition). Mosby. ISBN 0-323-01890-4
- Thomson Centerwatch: Drugs Approved by the FDA (Xeloda) Retrieved 6/05
- Mercier C, Ciccolini J (2007). “Severe or lethal toxicities upon capecitabine intake: is DPYD genetic polymorphism the ideal culprit?”. Trends in pharmacological sciences 28 (12): 597–598.doi:10.1016/j.tips.2007.09.009. PMID 18001850.
- “Subtopics”. Nice.org.uk. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
- Fingerprints May Vanish With Cancer Drug – US News and World Report
- Cancer Drug Erases Man’s Fingerprints – CNN
- “Stritch School of Medicine”. Stritch.luc.edu. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
- Xeloda.com (patient information, tools, and resources)
- OralChemo Advisor (patient information)
Capecitabine is an orally-administered anticancer agent widely used in the treatment of metastatic breast and colorectal cancers. Capecitabine is a ribofuranose-based nucleoside, and has the sterochemical structure of a ribofuranose having an β-oriented 5-fluorocytosine moiety at C-I position.
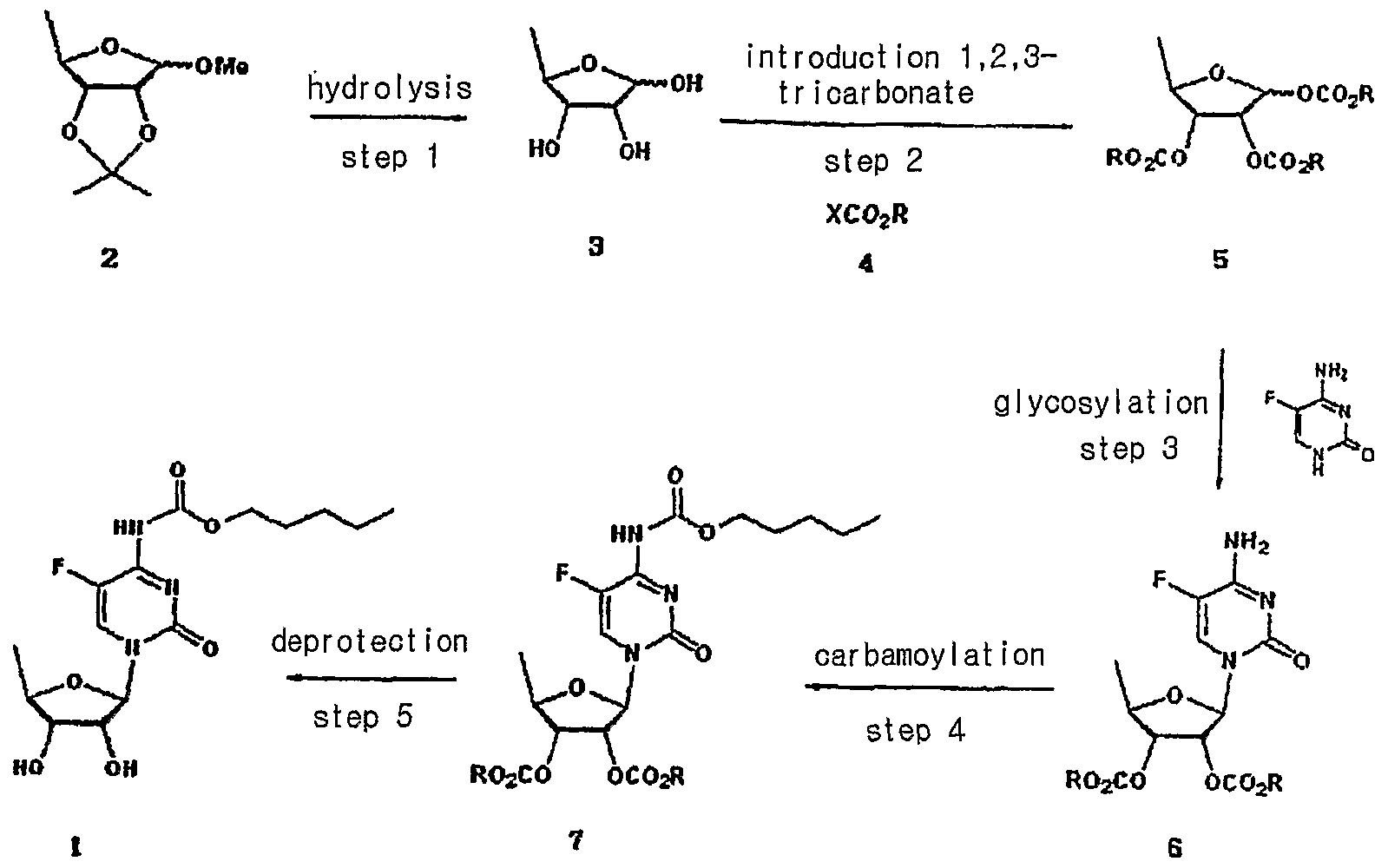
US Patent Nos. 5,472,949 and 5,453,497 disclose a method for preparing capecitabine by glycosylating tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranose of formula I using 5-fluorocytosine to obtain cytidine of formula II; and carbamoylating and hydrolyzing the resulting compound, as shown in Reaction Scheme 1 :
Reaction Scheme 1
1
The compound of formula I employed as an intermediate in Reaction
Scheme 1 is the isomer having a β-oriented acetyl group at the 1 -position, for the reason that 5-fluorocytosine is more reactive toward the β-isomer than the α-isomer in the glycosylation reaction due to the occurrence of a significant neighboring group participation effect which takes place when the protecting group of the 2-hydroxy group is acyl.
Accordingly, β-oriented tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranose (formula
I) has been regarded in the conventional art to the essential intermediate for the preparation of capecitabine. However, such a reaction gives a mixture of β- and α-isomers from which cytidine (formula II) must be isolated by an uneconomical step.
Meanwhile, US Patent No. 4,340,729 teaches a method for obtaining capecitabine by the procedure shown in Reaction Scheme 2, which comprises hydrolyzing 1-methyl-acetonide of formula III to obtain a triol of formula IV; acetylating the compound of formula IV using anhydrous acetic anhydride in pyridine to obtain a β-/α-anomeric mixture of tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-D-ribofuranose of formula V; conducting vacuum distillation to purify the β-/α-anomeric mixture; and isolating the β-anomer of formula I therefrom:
Reaction Scheme 2
III IV
However, the above method is also hampered by the requirement to perform an uneconomical and complicated recrystallization steps for isolating the β-anomer from the mixture of β-/α-anomers of formula V, which leads to a low yield of only about 35% to 40% (Guangyi Wang et al., J. Med. Chem., 2000, vol. 43, 2566-2574; Pothukuchi Sairam et al., Carbohydrate Research, 2003, vol. 338, 303-306; Xiangshu Fei et al., Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 2004, vol. 31, 1033-1041; and Henry M. Kissman et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1957, vol. 79, 5534-5540).
Further, US Patent No. 5,476,932 discloses a method for preparing capecitabine by subjecting 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine of formula VI to a reaction with pentylchloroformate to obtain the compound of formula VII having the amino group and the 2-,3-hydroxy groups protected with C5Hi1CO2 groups; and removing the hydroxy-protecting groups from the resulting compound, as shown in Reaction Scheme 3 :
Reaction Scheme 3
Vl VII 1
However, this method suffers from a high manufacturing cost and also requires several complicated steps for preparing the 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine of formula VI: protecting the 2-,3-hydroxy groups; conducting a reaction thereof with 5-fluorocytosine; and deprotecting the 2-,3-hydroxy groups.
Accordingly, the present inventors have endeavored to develop an efficient method for preparing capecitabine, and have unexpectedly found an efficient, novel method for preparing highly pure capecitabine using a trialkyl carbonate intermediate, which does not require the uneconomical β-anomer isolation steps.
synthesis

more info and description
Aspects of the present invention relate to capecitabine and processes for the preparation thereof.
The drug compound having the adopted name “capecitabine” has a chemical name 5′-deoxy-5-fluoro-N-[(pentyloxy) carbonyl] cytidine and has structural formula I.
H
OH OH I
This compound is a fluoropyrimidine carbamate with antineoplastic activity. The commercial product XELODA tablets from Roche Pharmaceuticals contains either 150 or 500 mg of capecitabine as the active ingredient.
tablets from Roche Pharmaceuticals contains either 150 or 500 mg of capecitabine as the active ingredient.
U.S. Patent No. 4,966,891 describes capecitabine generically and a process for the preparation thereof. It also describes pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating of sarcoma and fibrosarcoma. This patent also discloses the use of ethyl acetate for recrystallization of capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme I.
Scheme I
U.S. Patent No. 5,453,497 discloses a process for producing capecitabine that comprises: coupling of th-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-β-D-hbofuranose with 5- fluorocytosine to obtain 2′,3′-di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine; acylating a 2′, 3′- di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine with n-pentyl chloroformate to form 5′-deoxy- 2′,3′-di-O-alkylcarbonyl-5-fluoro-N-alkyloxycarbonyl cytidine, and deacylating the 2′ and 3′ positions of the carbohydrate moiety to form capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme II.
Capecitabine
Scheme Il
The preparation of capecitabine is also disclosed by N. Shimma et al., “The Design and Synthesis of a New Tumor-Selective Fluoropyrimidine Carbamate, Capecitabine,” Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 8, pp. 1697-1706 (2000). U.S. Patent No. 7,365,188 discloses a process for the production of capecitabine, comprising reacting 5-fluorocytosine with a first silylating agent in the presence of an acid catalyst under conditions sufficient to produce a first silylated compound; reacting the first silylated compound with 2,3-diprotected-5- deoxy-furanoside to produce a coupled product; reacting the coupled product with a second silylating agent to produce a second silylated product; acylating the second silylated product to produce an acylated product; and selectively removing the silyl moiety and hydroxyl protecting groups to produce capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme III. te
R: hydrocarbyl
Scheme III
Further, this patent discloses crystallization of capecitabine, using a solvent mixture of ethyl acetate and n-heptane. International Application Publication No. WO 2005/080351 A1 describes a process for the preparation of capecitabine that involves the refluxing N4– pentyloxycarbonyl-5-fluorocytosine with trimethylsiloxane, hexamethyl disilazanyl, or sodium iodide with trimethyl chlorosilane in anhydrous acetonitrile, dichloromethane, or toluene, and 5-deoxy-1 ,2,3-tri-O-acetyl-D-ribofuranose, followed by hydrolysis using ammonia/methanol to give capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme IV.
Scheme IV
International Application Publication No. WO 2007/009303 A1 discloses a method of synthesis for capecitabine, comprising reacting 5′-deoxy-5- fluorocytidine using double (trichloromethyl) carbonate in an inert organic solvent and organic alkali to introduce a protective lactone ring to the hydroxyl of the saccharide moiety; reacting the obtained compound with chloroformate in organic alkali; followed by selective hydrolysis of the sugar component hydrolytic group using an inorganic base to give capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme V.
Scheme V
Even though all the above documents collectively disclose various processes for the preparation of capecitabine, removal of process-related impurities in the final product has not been adequately addressed. Impurities in any active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) are undesirable, and, in extreme cases, might even be harmful to a patient. Furthermore, the existence of undesired as well as unknown impurities reduces the bioavailability of the API in pharmaceutical products and often decreases the stability and shelf life of a pharmaceutical dosage form.
nmr
1H NMR(CD3OD) δ 0.91(3H5 t), 1.36~1.40(4H, m), 1.41(3H, d), 1.68~1.73(2H, m), 3.72(1H, dd), 4.08(1H, dd), 4.13~4.21(3H, m), 5.7O(1H, s), 7.96(1H, d)

- The acetylation of 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine (I) with acetic anhydride in dry pyridine gives 2′,3′-di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine (II), which is condensed with pentyl chloroformate (III) by means of pyridine in dichromethane yielding 2′,3′-di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluoro-N4-(pentyloxycarbonyl)cytidine (IV). Finally, this compound is deacetylated with NaOH in dichloromethane/water. The diacetylated cytidine (II) can also be obtained by condensation of 5-fluorocytosine (V) with 1,2,3-tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose (VI) by means of trimethylchlorosilane in acetonitrile or HMDS and SnCl4 in dichloromethane..
-
- EP 602454, JP 94211891, US 5472949.
- Capecitabine. Drugs Fut 1996, 21, 4, 358,
- Bioorg Med Chem Lett2000,8,(7):1697,
- Capecitabine. Drugs Fut 1996, 21, 4, 358,
- EP 602454, JP 94211891, US 5472949.
-
Health.com -“There are various explanations why breast-feeding seems to preventbreast cancer,” Gonzalez-Jimenez said. “The most probable of these are …
- read all at
http://news.health.com/2013/08/15/breast-feeding-may-protect-some-women-against-breast-cancer/
By Kathleen Doheny
HealthDay Reporter