Pd/Cu-free Heck and Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction by Co nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic chitosan as reusable catalyst
Green Chem., 2017, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C6GC03377F, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/C6GC03377F, Paper
Abdol R. Hajipour, Fatemeh Rezaei, Zahra Khorsandi
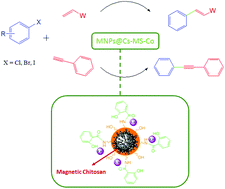
Chitosan (CS) is a porous, self-standing, nanofibrillar microsphere that can be used as a metal carrier. Amino groups on CS enable to modulate cobalt coordination using a safe organic ligand (methyl salicylate).
Chitosan (CS) is a porous, self-standing, nanofibrillar microsphere that can be used as a metal carrier. Amino groups on CS enable to modulate cobalt coordination using a safe organic ligand (methyl salicylate).
Pd/Cu-free Heck and Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction by Co nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic chitosan as reusable catalyst
aDepartment of Chemistry, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan 84156, Iran
E-mail: haji@cc.iut.ac.ir
Fax: +98 311 391 2350
Tel: +98 311 391 3262
E-mail: haji@cc.iut.ac.ir
Fax: +98 311 391 2350
Tel: +98 311 391 3262
bDepartment of Neuroscience, University of Wisconsin, Medical School, Madison, USA
Green Chem., 2017, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C6GC03377F

Department of Chemistry
Office : College of Chemistry, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan 84156, IR IranEmail : haji [AT] cc.iut.ac.ir or arhajipour [AT] wisc.eduPhone : +98 311 391xxxxFax : +98 311 391xxxxWeb Site : Prof. Abdolreza Hajipour
| EDUCATION: |
| 1970-1974 High School, Shahpour high school, Kazerun, IR, Iran |
| 1975-1979 B.S., Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, Isfahan University, Isfahan, I.R. Iran |
| 1981-1983 M.S., Organic Chemistry, Synthesis, Shiraz University, Shiraz, I.R. Iran |
| Thesis Title: “Synthesis of 2,6,7,11-Tetraphenyl Isobenzofuran B Cyclobutadiene” |
| Advisor: Professor Habib Firouzabadi |
| 1990-1994 Ph.D., Organic Chemistry, Wollongong University, Australia |
| Dissertation Title: “Asymmetric Synthesis of Chiral Amines and Benzazepine Alkaloids from Chiral Sulfoxides” |
| Advisor: Professor Stephen G. Pyne |
| POSITIONS: |
| 09/94-11/98 Assistant Professor, Isfahan University of Technology |
| 12/98-02/03 Associate Professor, Isfahan University of Technology |
| 03/03-present Professor, Isfahan University of Technology |
| 02/01-03/02 Visiting Scientist, University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, WI |
| 04/02-09/02 Associate Researcher, University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, WI |
| 10/02-1/05 Associate Scientist, University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, WI |
| 1/04 to present Senior Scientist, University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison, WI |

Chitosan (CS) is a porous, self-standing, nanofibrillar microsphere that can be used as a metal carrier. Amino groups on CS enable to modulate cobalt coordination using a safe organic ligand (methyl salicylate). This catalyst efficiently promotes Heck cross-coupling of a large library of functional substrates under mild and sustainable conditions (polyethylene glycol as solvent at 80 °C in a short time (1 h)). The cobalt complex was also used as a heterogeneous, efficient, inexpensive, and green catalyst for Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. The reactions of various aryl halides and phenylacetylene provided the corresponding products in moderate to good yields. More importantly, this phosphine, copper, and palladium-free catalyst was stable under the reaction conditions and could be easily reused using an external magnet for at least five successive runs without a discernible decrease in its catalytic activity.
Reaction yields were analyzed by gas chromatography (GC, BEIFEN-3420, detector type: FID, TCD equipped with Nukol™ capillary GC column, size × I.D. 30 m × 0.25 mm, df 0.25 μm). 2,3-Dimethylnaphthalene as was used as internal standard. The gas flow rate of 2 mL min-1; and oven temperature at 80 oC for 15 min and then increased to 170 oC.


General procedure for catalyst preparation The magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were prepared according to the method reported in literature64 based on the precipitation of magnetite nanoparticles from a mixture of iron(III) chloride and iron(II) sulfate by ammonia (25% solution in water). Subsequently, in a round-bottom flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer and condenser, a mixture of magnetic nanoparticles and sodium sulfate (20%, w/v) was added to a solution of chitosan (1%, w/v) in acetic acid (2%, w/v) under stirring. Stirring was continued for 1 h to obtain the aqueous suspension of MNPs/CS. Then, the magnetic nanoparticles were separated from the reaction mixture by an external permanent magnet, washed with ethanol and methanol several times, and dried under vacuum at 70 °C. For the preparation of supported methyl salicylate ligands, a solution of ethanol suspension of MNPs/CS (1.5 g per 10 mL) was added to methyl salicylate (6.5 mmol), and the mixture was stirred at 60 °C for 24 h. The final Co-MS@MNPs/CS was obtained as a brown solid by the addition of CoCl2·6H2O (4.2 mmol) dissolved in 10 mL of ethanol to disperse the mixture of MNPs/CS-MS (1.01 g) in ethanol (5 mL) and stirred at 60 °C for 18 h. The resulting complex was collected by an external permanent magnet, washed with ethanol (3 × 10 mL) to remove the unreacted materials, and finally dried in air (89% yield based on the amount of Co in the catalyst determined by ICP).
General procedure for the Heck reaction In a round-bottom flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, a mixture of K3PO4 (4 eq.), olefin (1.1 mmol), and aryl halide (1 mmol) in PEG (3 mL) was added to 5 mg of catalyst (1.1 mol% of Co) and the flask was equipped with a condenser for refluxing. The abovementioned mixture was heated at 80 °C in an oil bath. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC (hexane/EtOAc, 80 : 20) and gas chromatography (GC). After the completion of the reaction, the mixture was diluted with dichloromethane and water. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by column chromatography. The products were characterized by comparing their physical properties, such as m.p., IR, 1 H, and 13C NMR spectra, with those reported in literature
General procedure for Sonogashira reaction In a round-bottom flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, phenyl acetylene (1.2 mmol), aryl halide (1.0 mmol), catalyst (10 mg), and KOH (2 eq.) in DMSO (3 mL) were stirred under an air atmosphere at 140 °C. The progress of the reaction was monitored using TLC and GC. After the completion of the reaction, the mixture was diluted with dichloromethane and water. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The product was isolated by column chromatography to afford the corresponding products in 55–80% yields. The products were characterized by comparing their physical properties, such as m.p, IR, 1 H, and 13C NMR spectra with those reported in literature.
////////////