DOI: 10.1039/C3GC41799A, Communication
This synthesis was confirmed to follow the GAP chemistry process, which can avoid traditional chromatography and recrystallization purification methods.
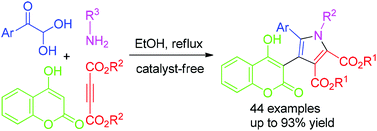
GAP chemistry for pyrrolyl coumarin derivatives: a highly efficient one-pot synthesis under catalyst-free conditions
A concise and efficient one-pot synthesis of pyrrolyl coumarin derivatives via a four-component reaction of 4-hydroxycoumarin, arylglyoxal monohydrate, dialkyl but-2-ynedioate and amines under catalyst-free conditions in an environmentally friendly medium (ethanol) is described. This synthesis was confirmed to follow the group-assisted-purification (GAP) chemistry process, which can avoid traditional chromatography and recrystallization purification methods
spectra
R2 = 3 CHLOROPHENYL
R1= METHYL
dimethyl 1-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-(4-hydroxy-2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrole-2, 3-dicarboxylate (5c).
The reaction of 4-hydroxycoumarin 1 (16.2 mg, 1 mmol), phenylflyoxal monohydrate 2a (15.2 mg, 1 mmol), dimethyl but-2-ynedioate 3a (14.2 mg, 1 mmol) and 3-chloroaniline 4c (12.7 mg, 1 mmol) in ethanol (5 mL), at 80 °C 1.5 h, afforded 46.0 mg (87 %) of 5c.
white powder; m.p.: 242-246°C; IR (KBr, ν, cm-1): 3423, 3075, 3002, 2951, 2853, 1720, 1683,
1577, 1483, 1444, 1303, 1271, 1213, 1126, 1077, 1043, 1013, 988, 924, 880, 761, 698, 649; 1
H NMR (DMSO-d6, 400 MHz): δ 11.29 (s, 1H, OH), 7.76 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.55 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, ArH), 7.40-7.18 (m, 6H, ArH), 7.10-7.02 (m, 5H, ArH), 3.63 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.60 (s, 3H, OCH3); 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz): δ 164.28, 162.30, 162.20, 161.52, 152.91, 139.00,
138.22, 133.24, 132.88, 130.87, 130.27, 129.99, 129.21, 128.80, 128.44, 128.35, 127.59, 127.38,
124.48, 124.09, 119.89, 116.64, 116.16, 113.35, 98.28, 52.89, 52.18; HRMS (ESI) calcdforC29H2035ClNO7 [M]+: 529.0928, found: 529.0933
ジャージ ニューバランス グレー レディース http://www.iosdjhnsa.com/