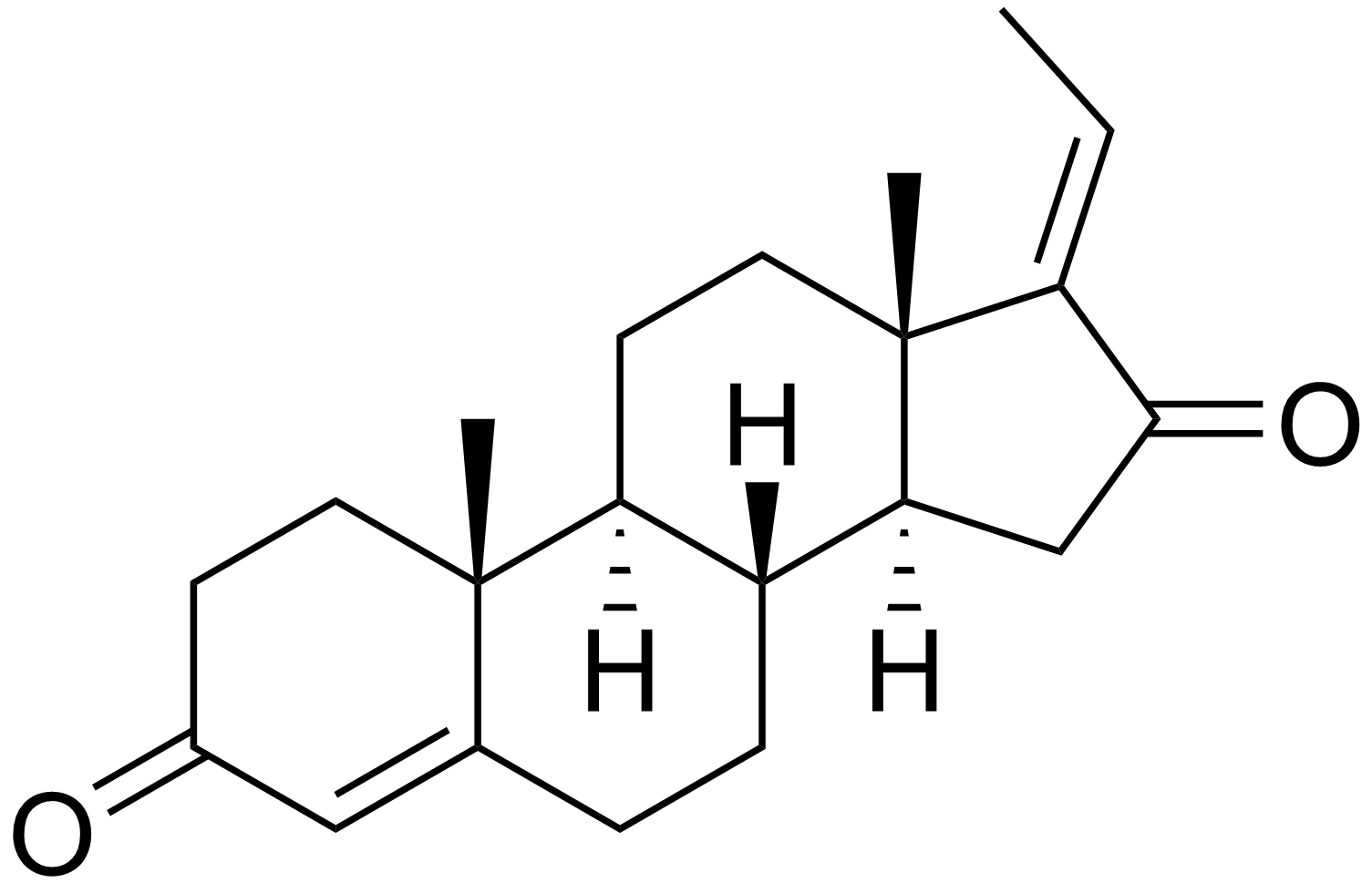
E-Guggulsterone

Z-Guggulsterone
http://www.omicsonline.org/2161-0444/2161-0444-2-e105.php?%20aid=9899
Citation: Xiao M, Xiao D (2012) Gugulipid, an Extract of Ayurveda Medicine Plant Commiphora Mukul as a Potent Agent for Cancer Chemoprevention and Cancer Chemotherapy. Med chem 2:e105.
doi:10.4172/2161-0444.1000e105
Department of Urology, University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15232, USA
| Gugulipid (GL), an extract of Commiphora mukul, has been safely used for thousands of years in the Indian Ayurveda medicine practice for the treatment of different ailments and has been used recently in many clinical trials that focused on its cholesterol-lowering effect. GL has recently been paid great attention for its cancer chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic potential. Z- and E-Guggulsterone have been identified as the major active components of GL. Studies have shown that GL as well as Guggulsterones can inhibit cancer growth in vitro and in vivo and lead to prevention of cancer initiation, promotion and progression. Although the action mechanisms of GL are not completely understood, GL has been revealed as a multitargeted cancer chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agent. The increased understanding of the anti-cancer activity of GL and its molecular targets would allow us to improve its efficacies in different types of human cancers by single and/or combination strategies. | |||||
Gugulipid (GL, guggul, guggal, or gugul lipid) is the ethyl acetate extract of gum guggul resin (raw material) that is harvested directly from the Commiphora mukul tree (family name: Burseraceae; synonyms: Hook, Bandari, Balsamodendron mukul, and Commiphora Wightii). GL is a highly valued botanical medicine. As aforementioned, GL has been safely used for thousands of years in the Indian Ayurvedic medicine for the treatment of different ailments, including lipid disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcers, osteoarthritis, bone fractures, epilepsy and obesity . In 1986, GL was granted approval in India for marketing as a lipid lowering drug (Indian Pharmacopeia 2007: pgs. 2038-2040). Several products of standardized formulations of Commiphora mukul are already in human use as cholesterollowering agents . The Z- and E-forms of guggulsterone (Gug, 4,17(20)-pregnadie-3, 16-dione) have been identified as major active components of GL . GL and its active component z-Gug have been used in many clinical trials that focused on its cholesterol-lowering effect . Numerous studies continue to support that many edible phytochemicals have cancer chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic potential . These finding motivated the investigation of the cancer chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic potential of GL and its active components.Guggulsterone is a plant steroid found in the resin of the guggul plant, Commiphora mukul. Guggulsterone can exist as either of two stereoisomers, E-guggulsterone and Z-guggulsterone. In humans, it acts as an antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor, which was once believed to result in decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Several studies have been published that indicate no overall reduction in total cholesterol occurs using various dosages of guggulsterone, and levels of low-density lipoprotein (“bad cholesterol”) increased in many people.[1][2] Nevertheless, guggulsterone is an ingredient in many nutritional supplements.
Scheme 1. Stereoselective synthesis of E-guggulsterone (1) from 4-androsten-3,17-dione (5). (i) CH(OEt)3, p-TSA, THF/EtOH, quantitative; (ii) EtPPh3Br, t-BuOK, THF, reflux; (iii) HCl, THF, 95% from 6; (iv) SeO2, t-BuO2H, 90%; (v) (COCl)2, DMSO, Et3N, CH2Cl2, 85% |
|||||
